
Geometrics Of Aquifers -
By WaterLocating.Com
This is a technical paper of the inner matrix of an aquifer.
An aquifer system consists of porous rock and or fracture systems that contain a degree of water that has the ability to conduct. That is, to flow. Water within an aquifer may only move inches to hundreds of yards within a year. Mostly it is inches, until a passage is produced (well bore hole), that will give the water an escape from its confined environment.
The percentage of water that conducts to your well is dependant upon the interstitial fabric of the aquifer system. Compressional factors, number of interconnecting fractures systems, and the porosity of the granitics or alluvium determine this fabric factor.
Alluvium is associated with sandy deposits, unconsolidated earth that compares to river basins and the bottom of canyons which are normally sedimentary in formation, cemented over time into rock volumes and fragmented to a fair degree.
Alluvium can be seen as fill dirt occupying a cavity MASKING ancient topographic expression.
Beneath this alluvium within the geomorphic expression (subsurface signature), lies the fracture signature leading to the more promising area within the aquifer for a sustained recharge rate.
To add a little more technical insight as to the composition of aquifers... within the porous granitics are fractures, microscopic to hundreds of meters in length that are connected to major interfacial fractures. These fracture zones are fed with water from adjacent interstices that have basically no movement, except for the permeability of the porous medium in which they rest.
Computer Profiles will target these zones, called The Hydrogeological Zones.
See profiling that is associated with certain testimonials, the black zones.
The black porous zones collects more water than the white harder rock zones.
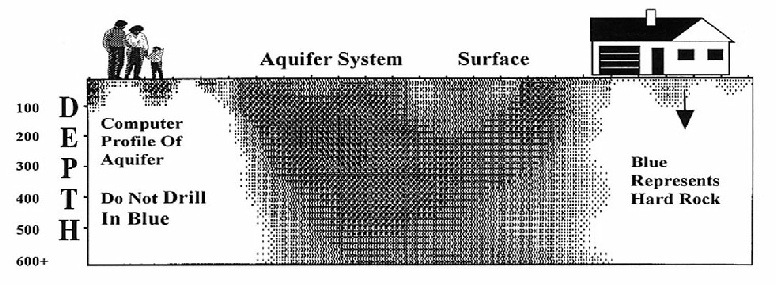
Black zones are the more porous and fractured granitics that comprise your aquifer, which is being supplied with water by a maze of interconnected fractures with interstices that lead to your new water well bore hole.
For high capacity water wells you "MUST" target the more highly fractured "Hydrogeological Zones." Aquifer Video 4 of 4
This confined environment basically duplicates the geometric framework that is in the subsurface of river basins.
This is the reason why water wells in river basins, drilled anywhere within the basin, produce a fair amount of water.
River basins are sedimentary unconsolidated type formations, which are highly fragmented, allowing for high permeability.
The “Heart of The Aquifer” is high permeability, equates to increased GPM.
This fragmented type of geometry can now be identified within the solid granitics of your subsurface with computers.
The combination of both qualitative and quantitative analysis of the generated parameters from WaterLocating's profiling permits one of the most accurate assessments of aquifer geometrics.
Employing WaterLocating's analysis will help identify optimum drilling targets within potential water-
This will maximize the water potential of your parcel to achieve
the water requirements for your new water well.
Aquifer systems, in general, are a minimum of 400 feet wide.
Fractures within aquifer systems are not totally inter-
Two wells within a few feet or a few hundred feet of each other having different GPM are in the same aquifer system but drilled into different fracture zones.
Specializing in Aquifers
www.WaterLocating.Com
760 . 742 . 3727
| Scientific |
| Sprinkler |
| Videos |
| Videos 1,2,3,4 |
| Vista Ca 2014 |
| Drillers Testify |
| Ramona Videos |
| Video 1 of 4 How It Works (Important) |
| Video 2 of 4 Lineament Analysis |
| Video 3 of 4 Water-Witching & EKS |
| Video 4 of 4 Aquifer Geometrics |
| Vista Video |
| Testimonial |
| San Diego |
| Riverside |
| Los Angeles |
| Alpine |
| Bonsall |
| Descanco |
| El Cajon |
| Escondido |
| Fallbrook |
| Jamul |
| Julian |
| Lakeside |
| Pauma Valley |
| Poway |
| Rainbow |
| Ramona |
| Santa Ysabel |
| Valley Center |
| Warner Springs |
| Ramona Video |
| Anza |
| Aguanga |
| Benton Area |
| Hemet |
| La Cresta |
| Murrieta |
| Perris |
| Temecula |
| Acton |
| Agua Dulca |
| Santa Clarita |
| Aquifers |
| San Diego |
| Riverside |
| San Bernardino |
| Los Angeles |
| Pivot Farms |
| About Us |
| Drillers Testimonial |
| Do's & Don'ts |
| Dud Wells |